This lesson is based on teachcomputing.org lessons.

Today, you are going to….
- learn about domain names and URLs
- Learn about IP addresses, and DNS
- explain that internet devices have addresses
- describe how computers use addresses to access websites
1.
Let’s investigate further how the internet works!

How The Internet Works? | What Is Internet? | Dr Binocs Show | Kids Learning Video | Peekaboo Kidz. (6:29 minutes long)
How does the internet works? | Kids Educational Video | What is the internet | Smartie Alpaca Learn. (2:22 minutes long)
2.
Internet data transfer
Computers can share a variety of different media types over the internet.
Every time you access a website, send a message, or watch a video online, your computer sends and receives data from another computer.
- You use a website address, also known as a domain name or an URL
- A system called DNS matches the website’s address to its IP address
So, computers communicate with each other over the internet!
3.
PROTOCOL
Digital devices have certain rules (protocols) for how they communicate with each other. (A protocol is an agreed way of doing something.)

We can also say that a “protocol” specifies the method of communication, or indicates how the resource will be accessed.
For example, a message may be send as HTTP, or as HTTPS.
4.

What on earth is HTTP and HTTPS?
HTTP is a protocol used to send data between a web browser and a website.
HTTP stands for Hypertext Transfer Protocol.
HTTPS stands for Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure.
HTTP messages are sent as plaintext, which means unauthorized people can easily access and read them over the internet.
In contrast, HTTPS is a secure version of HTTP. (HTTPS is encrypted in order to increase security of data transfer.)
5.
So, how does a computer know where to send data? Computers use special addresses!

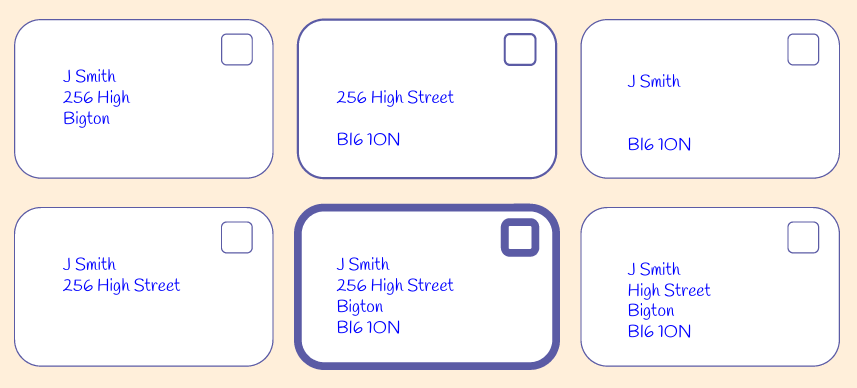
It works similar to when we send a letter from one person to another person.
All of the information in the address is needed to make sure the letter gets to the right place, and to the right person.
Correct addresses on letters include a name, street name, town, and postcode.

Which of these letters do you think will reach the person at their destination?

ANSWER

This one definitely will!
It has a name, street address, town, and postcode.
6.
Domain Names
A website’s address is also known as a domain name.
URL
The address of a specific page on a website is known as the URL. (It is the detailed address for accessing a specific web page, file, or video.
IP Addresses
Each device, each website, and each server has an address, called an IP address.
So, IP addresses tell us where a device is, where a website is hosted, and where a server is.
Humans use domain names, but computers use IP addresses!
DNS
A special computer matches the IP addresses to the domain names.
This computer is called a Domain Name System, or DNS.
7.

Domain Names
A website’s address is also known as a domain name.
Look at this web address:
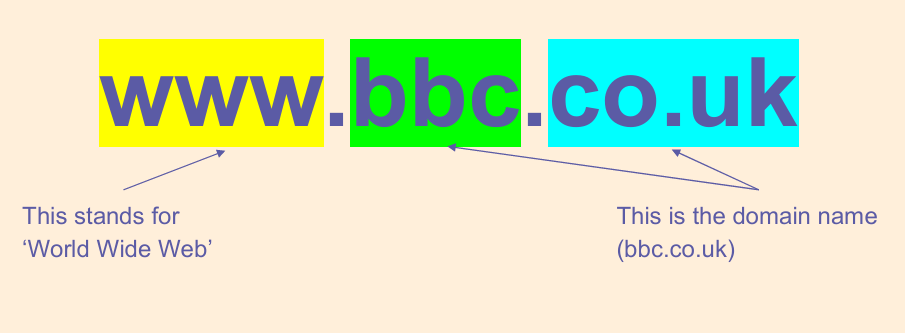
The address of the website tells you where it was created.
Where were these websites created?

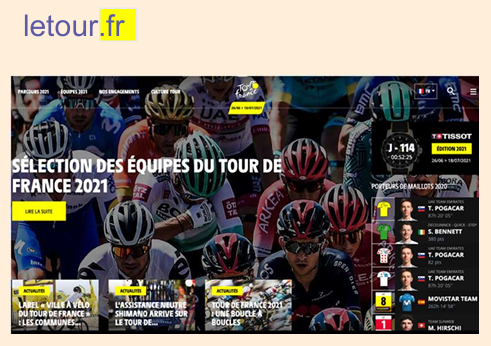

UK
United Kingdom
Fr
France
8.
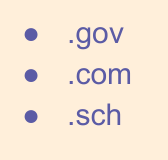
Here are the ends of some web addresses. Some tell you where the website may originate from. Where do you think these are from?



Some tell you more about the content of the website. What do you think these mean?


9.

URLs
A website’s address is called the domain name, but a website’s address can also be a URL.
One of the major differences between URLs and domains is that URLs are specific while domains are general.
A URL describes a single page on the internet.
A domain refers to many web pages that connect to form an entire website.
URL (Uniform Resource Locator)
A URL is the complete address used to access a specific resource on the internet, such as a web page, file, or video. (It tells a browser where to go to find a specific page or file.)

A URL is made up of several parts:
- The Protocol indicates how the resource will be accessed. (It specifies the method of communication.) (e.g.,
http://,https://) - The Domain Name identifies the website. (It is the human-readable name of the resource’s host.) (e.g.,
www.example.com) - The Path specifies a specific page or file on the website. (It gives the exact location of the resource on the host server.) (e.g.,
/about/page1)
10.

IP Addresses
Each device, each website, and each server has an address, called an IP address.
So, IP addresses tell us where a device is, where a website is hosted, and where a server is.

Humans use domain names, but computers use IP addresses.
Computers use special addresses called IP addresses, which are structured like this:

(IP stands for Internet Protocol.)
Computers use IP addresses to identify each other on a network.
When computers send messages, they have the address they’re sending TO, and the one it’s coming FROM.
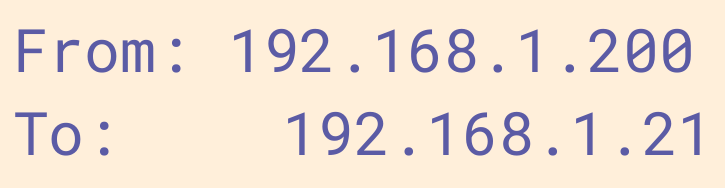
When a message is sent from one computer to another over a network, both the destination and start addresses are included.
Why do you think that is?
ANSWER

So that the computer knows where to reply!

11.
By now you should know that:
- A website’s address is known as its domain name
- A specific page (or file) on a website has an address known as the URL
- Each website also has an IP address
- Each website is hosted on a web server
- (Each server, and each device, also has an IP address.)
12.

DNS
A special computer matches the IP addresses to the domain names.
This computer is called a Domain Name System, or DNS.
Humans use domain names, but computers use IP addresses. A special computer matches IP addresses to the domain names. This computer is called a…
Domain Name System (DNS)
(So, a Domain Name System is a computer that works like an address book: it matches IP addresses to the domains!)

Do you remember what a Data Centre is?
A Data Centre is where data gets stored. A Data Centre hosts websites, as well as the “phonebook” (or DNS).
13.
The DNS is like the “phonebook” of the internet!
Humans use domain names (like www.example.com) to identify a website, but computers use IP addresses (e.g., 192.0.2.1).
A DNS finds the IP address (e.g., 192.0.2.1) of the human-readable domain name (e.g., www.example.com).
Without the DNS, you would need to remember the numerical IP address of every website!
14.

- a websites address is known as its domain name
- we know websites by their domain names
- a webpage has a specific address called the URL
- every website is hosted somewhere on a web server
- every website also has its own IP address
- a DNS (Domain Name System) matches the website’s domain name with its IP address
When you go to the website http://www.raspberrypi.org, a DNS server looks up the IP address of this website and directs your computer to the website’s server.
15.

Find the IP addresses of the websites on the activity sheet.

HOW?

You need to look up the IP Addresses by clicking on the link below. When you enter the domain name, you will be provided with the corresponding IP address.
You will get results that looks like this:
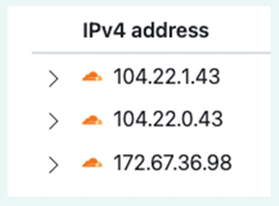
What do you notice about the IP addresses for google.com and youtube.com? Can you explain what you have noticed?
ANSWER

The IP addresses of google.com and youtube.com are similar. The IP addresses of these 2 websites show us that they are both in the same location! That is because YouTube is owned by Google – so, it is hosted on Google servers.
16.

DNS
DNS stands for Domain Name System. It turns domain names into IP addresses. This allows browsers to get to websites and other internet resources. Every WEBSITE AND EVERY device on the internet has an IP address, which other devices use to locate each other.
The DNS, or the domain name system , is the phonebook of the Internet, connecting web browsers with websites. The DNS matches human-readable domain names (e.g., www.example.com) with IP addresses (e.g., 192.0.2.1), which are used by computers to identify each other on the network.
IP Address
IP address stands for Internet Protocol Address. It is a unique address for a device connected to a network (like the internet). It enables devices to communicate with each other by addressing packets of data to the correct destination.
- IPv4: The most common format, consisting of four sets of numbers (e.g., 192.168.1.1).
- IPv6: A newer format designed to handle more devices, using hexadecimal notation (e.g., 2001:0db8:85a3:0000:0000:8a2e:0370:7334).
LAN
LAN stands for Local Area Network. It is a network that connects computers and devices within a localized area, such as a home, office, or building.
WAN
WAN stands for Wide Area Network. It is a network that covers a large geographical area, often connecting multiple LANs. The internet itself is the largest example of a WAN.
URL
A URL stands for Uniform Resource Locator. It is the complete address used to access a specific resource on the internet, such as a web page, file, or video. It tells a browser where to go to find a specific page or file.

This is the original lesson source:
(WordPress advertisements may appear below.)

