
World War Two
Today we are going to look at the “home-front” in more detail…
1.



One can easily think that the ‘Home Front‘ must have been a safe place, but it was not because bombing raids destroyed homes and killed many people.
Everyone tried to help in the ‘war effort’. For example, because men were now fighting in the war, women helped to do a variety of jobs that would usually be done by men.
Men who were not fighting in battles on the main land did a variety of jobs on the home front. For example, some were ARP Wardens and other served in the Home Guard.
2.
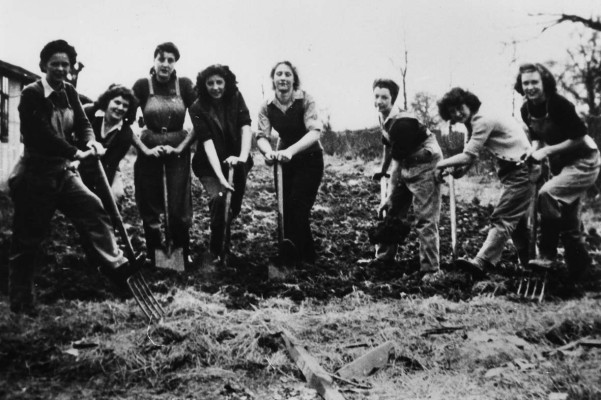

Let’s start by looking how women helped in the ‘war effort’ during WW2. Women help on the home front as “Land Girls”. This meant that they worked as farm workers.
With the men fighting on the battle fronts, more help was needed on farms in order to increase the amount of food grown within Britain. So, the government started what was called the Women’s Land Army.

Here are some of the jobs the Land Army had to do:

Women also had to do other important jobs. Here is a long list of some of the jobs women did during the war:


Before the war, job opportunities for women were limited, as most women were ‘housewives’. Those who were employed elsewhere were mainly nurses, domestic servants, or shop assistants.
However, as men joined the army to fight, women were called upon to fill their jobs.
3.

Let’s see what else we can learn about the role women played during the war.
How 80,000 women prevented… starving during WWII. (4:15 minutes long)
4.
And here is a fun song telling us more about women and WWII…

The WWII Girls Song. (2:16 minutes long)
5.

Let’s now also look at some of the jobs men did on the home front. For example, some men were ARP Wardens, and others were part of the Home Guard.
6.

The ARP Wardens supervised the Blackout – they had to protect civilians from the danger of air-raids. (ARP stands for Air Raid Precaution.)


One could recognise an ARP Warden by the helmet: they wore helmets with a big W on the front.
So, what exactly did ARP Wardens have to do?


Around 200,000 people volunteered to become ARP wardens. Some women were also ARP wardens. Eventually there were 1.4 million ARP wardens in Britain. Most ARP wardens were part time volunteers who had full time day jobs.
7.
Watch the following video clips to learn more about the ARP Wardens.

-1-
Liverpool ARP Warden. (2:16 minutes long)
-2-
Air Raid Warden. (3:50 minutes long)
8.

The Home Guard were volunteers who defended the five thousand miles of Britain coastline in case of invasion by Germany. Some of these men were in their sixties!

The men were given military style training. At first, they had no uniforms and little equipment. The public were invited to give their shotguns and pistols to the Home Guard and within a few months over 20,000 weapons were handed in. Many of the men made their own weapons too.

Who joined?
Many of the men who joined the Home Guard were those who could not join the regular army because their day time jobs were necessary to keep the country running. They included farm workers, bakers, teachers, grocers, bank staff and railway workers.
Other men who joined were either to young or too old to join the regular army.
In 1942 the Women’s Home Guard Auxiliaries were formed, and women were able to work with the Home Guard.
So, what exactly did the Home Guard have to do?


9.
Here are five top facts about the Home Guard!

The Home Guard – Top 5 Facts. (3:23 minutes long)
10.

Complete the following worksheet to test your understanding of jobs that people did on the Home Front during WWII.



SOLUTION

11.

Useful Links for WW2:
—WORKBOOK—
———-
—ADDITIONAL MATERIAL—

You may be asked to complete more tasks in your WW2 Workbook!
——-&——-

(WordPress advertisements may appear below.)









